Consistently seen to be not only the most popular but also the most profitable altcoin – Ethereum deserves your attention.
Well, now that we have your attention, it’s probably important to note that ether, not ethereum is the popular altcoin. While ethereum and ether seem to be used interchangeably most of the time, the fact is that ether is the cryptocurrency that’s associated with Ethereum – a distributed computing platform. To keep things straight if you’re new to altcoins, it’s always wise to seek the help of a trading platform geared towards beginners, like Bitvavo.
Stay with us, it gets weirder.
How it All Started
Vitalik Buterin, a programmer and co-founder of Bitcoin Magazine argued that bitcoin wasn’t reaching its potential. While the well-known cryptocurrency is fairly ideal for processing straightforward monetary transactions, it’s incapable of imposing any type of terms or conditions onto the system of payment. Meaning, that you can send and receive bitcoin, but you can’t request specific tasks to be executed in exchange for these coins. Or you can, but there’s no way of enforcing that either the tasks will be done, or the fees will be paid.

This is where Buterin made clear that he believed that Bitcoin needed a scripting language in order to create applications and contracts and Ethereum was born. While Ethereum began to develop in 2013, it wasn’t released until early 2015. Since that time, Ethereum has stuck to its initial premise of continually updating and upgrading its product to ensure usability, functionality, security, and decentralisation.
As opposed to the Bitcoin hard forks that have created much controversy and less than memorable offshoots of the coin, Ethereum releases prototypes for beta-testing. During beta-testing, the Ethereum network offers “bug bounties” for any users willing to stress test the proposed system update and its limits. Making beta-testing the new platforms incentivised.
While the network has seen their share of hard forks, they exist only in response to cyber attacks, as opposed to differing viewpoints on how the system should work.
Offering What Bitcoin Can’t
The progression of the program itself isn’t the only way in which Ethereum differs greatly from its predecessor, Bitcoin.
Ethereum Virtual Machine
While Ethereum can offer a transfer of monetary value through the use of ether – it’s a unique cryptocurrency – the network is truly designed to be something more. The ethereum network is what is considered a “distributed computing system”.
This means that much like in Bitcoin, millions of computers around the world are connected to a general network. These computers (called “nodes”) all interact with one another via messages or “instruction sets”. These instruction sets identify a common goal that all of the nodes are capable of working on cooperatively. This decentralised network is called the “Ethereum Virtual Machine”.
What makes this virtual machine so incredibly useful and unique is that it’s “Turing-complete”. This means that each computer is capable of understanding, executing, or recognising other types of instruction sets or programming languages. Meaning a computer in Istanbul is capable of simulating the same data requests as a computer in Zimbabwe… or Lima… or Boston, London, Toronto, and so on. Meaning that any node within the virtual machine is just as capable of carrying out a specific task as any other node.
Smart Contracts
This virtual machine really shows its versatility and usefulness when it comes to smart contracts. The name can sometimes be a bit misleading, as these contracts aren’t really “smart” but specifically programmed to execute certain functions without the use of an intermediary.
This is basically just a fancy way of saying that instead of using some human arbiter to ensure the terms and conditions of any agreement are carried out- a computer program does it instead. This not only saves people time and money but is infallible, as one step cannot continue without a previous step being carried out and verified first.
Imagine yourself walking up to a souvenir penny machine. These machines take a penny, squish a fancy pattern on to it, and allow you to bring home a fun piece of nostalgia back from your holiday. In order to get that coveted squished penny, a person must first insert payment (we’ll say about 50 cents) and a penny to be squished. Once the coins are accepted by a machine, the person then chooses their favorite design. The chosen design is then stamped onto the penny and it is delivered to the person.
You can’t walk away with a souvenir penny without choosing a design. There’s no way you could possibly choose a design without a penny to put it on, and you most certainly won’t get that penny accepted to be squished in the first place if you don’t pay your 50 cents. There’s no way to move from one step to another without completing each step in a sequence. This is how smart contracts work. Each term or condition must be met and verified before moving onto the next step. Each step must be completed in the order given to finish out the contract in which each party leaves with their purchase or their money.
Gas Computational Metering
Ether, the cryptocurrency associated with Ethereum, is much more than just another type of digital currency. In fact, it oftentimes works much more similar to a token one that pays for something called “gas”.
Gas is one other thing that enables Ethereum to create novel and dynamic agreements, as instead of paying directly for a service or product, ether is used to pay for the computational effort required in order to execute any specific contract. Much like we a meter to tell us how much we need to pay for water usage, gas is a system of measurement used to calculate the cost of computational effort.
Once the amount of gas required to execute any particular function is computed, a user then pays for that function in ether. However, it is a pay-before-you-go system. So, keeping in mind that gas is simply a unit of measurement, it is applied similarly in the way that you would think about using gasoline to go on a road trip. If you have a destination you’d like to get to, you must first go to a service station and fill up your car’s tank with gasoline in order to get to that destination.
However much gas would be required to fully execute all the steps of a smart contract, from start to finish, is calculated before the computation begins. Ether is then paid to the programmer who will be coding the contract, and as long as you have enough gas in the tank, the contract is then carried out in full.

 Features3 years ago
Features3 years ago
 Bitcoin2 years ago
Bitcoin2 years ago
 Features3 years ago
Features3 years ago
 Features3 years ago
Features3 years ago
 Features3 years ago
Features3 years ago
 Features3 years ago
Features3 years ago
 Features8 months ago
Features8 months ago
 Bitcoin10 months ago
Bitcoin10 months ago



















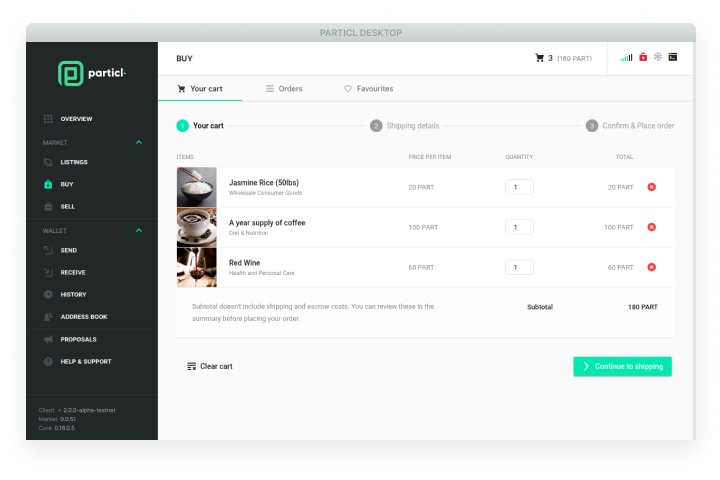
 Cryptocurrencies can be difficult to spend on a day-to-day basis and
Cryptocurrencies can be difficult to spend on a day-to-day basis and 
